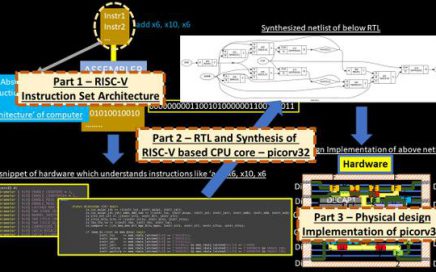
RISC-V enters India and VSD personally invite you…
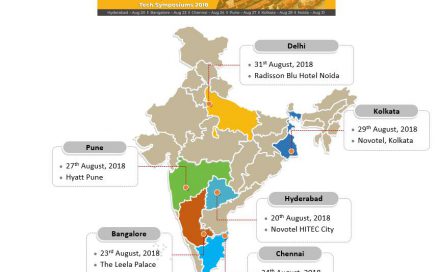
We would like to invite you to attend one of the SiFive & Open-Silicon Tech Symposiums taking place at six different locations throughout India in August. See map in below image for exact locations and date of events.
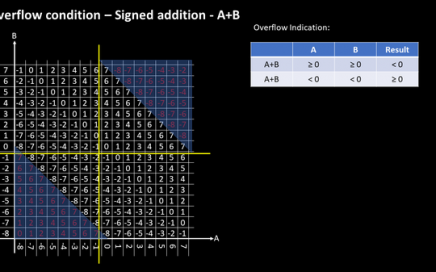
I would be presenting a very important tutorial, which closely connects open-source ISA implementation to open-source EDA tools – “How to design complex RISC-V SoC with open-source EDA tools and time to productize design ideas?”