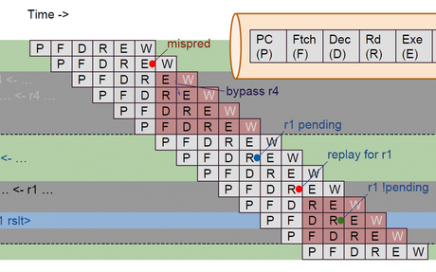
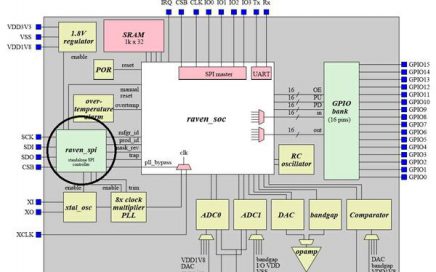
VSDOpen2022 – Ground-level efforts to boost Semiconductor tapeouts and Skill Development
VSDOpen conference is an attempt to bring out some cutting-edge activities especially around open-source EDA with a special focus on skill development using open and proprietary tools. VSDOpen also focuses on milestones achieved by VSD in the past year, and some interesting projects which VSD will be working on in the next year. It’s like the VSD Annual Hands-on meeting where everyone is invited for free and allowed to rate us for our work 🙂