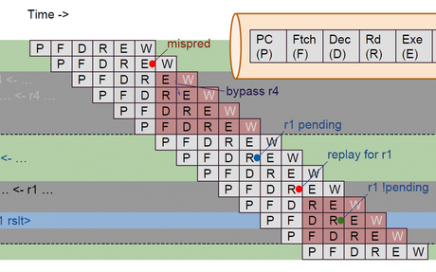
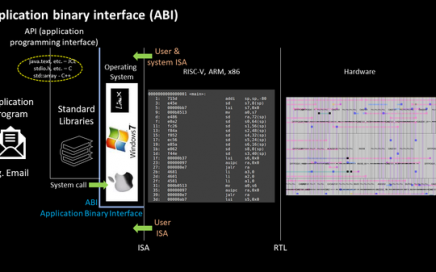
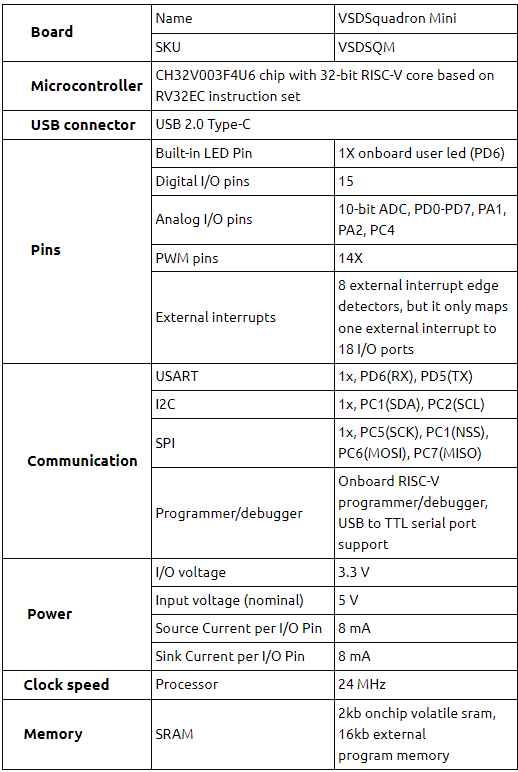
TAU 2019 Contest Announcement
Timing-driven optimization is imperative for the success of closure flows. The optimization engine applies changes to the design and estimates circuit delays quickly and accurately to improve timing, area, and power performance. This procedure is inherently complex and computationally challenging.